Preliminary study on steel barrel welding process (1)
Preliminary study on steel barrel welding process (1)
Sinopec Sales Company North China Company Tianjin Co., Ltd. Sun Lianhe
Over the past ten years of reform and opening up, China's steel drum industry has achieved unprecedented development, and the technology and technological level of steel drum production have been greatly improved. At present, resistance contact welding has been widely used in the steel barrel welding work of various steel drum enterprises. Through the work practice, various steel drum manufacturers have accumulated a wealth of experience in the relevant technology of the resistance welding process. In order to continuously improve the welding process level in the production of steel drums, it is urgent to carry out extensive technical exchanges on the experience gained in the application of resistance welding, and this article will be used for reference.
Compared with other welding methods, resistance welding has the advantages of high productivity, low cost, material saving, easy automation and good working conditions. Therefore, it is widely used in industries such as automobiles, tractors, airplanes, bicycles, and household appliances. At the same time, our steel drum industry also applies it to the welding work of all welded parts of steel drums. For example, straight seam welding of steel drums is first spot welding, then seam welding (roll welding); barrels of barrels The mouth is welded to the flap by a projection welding method. These welding jobs are typical of resistance welding.
What is resistance welding? We put the workpiece to be welded between the two electrodes and press it with electric current, which is heated by the heat generated by the resistance of the workpiece to form a local melting (or plastic state). After the power is cut off, the pressure is continued to form a firm The welding process is called resistance welding.
Below, we discuss the problems of resistance welding classification, basic rationale, selection of lap joints, electrode and weldability analysis of steel plates.
First, the classification of resistance welding
There are many types of resistance welding, which can be generally classified according to the type of joint, the process, the current, and the type of power source.
1. According to the connector form: can be divided into lap resistance welding and butt resistance welding.
2. According to the process: it can be divided into spot welding, seam welding, projection welding and butt welding.
3. According to the type of current: can be divided into AC welding, DC welding and pulse current welding.
4. According to the power source energy: can be divided into capacitor energy storage and magnetic field energy storage.
The above classification can be expressed in Table 1.
Table 1
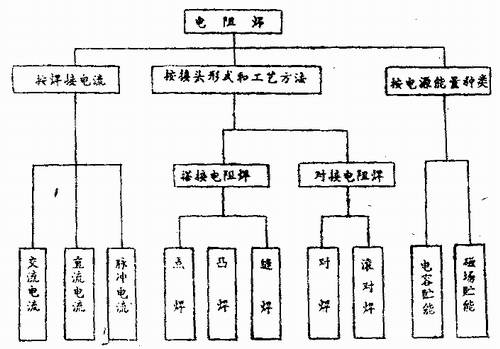
Spot welding, seam welding and projection welding used in steel drum production are all lap resistance welding. The domestically produced FN1-150-5 seam welder and the automatic welder produced by British United Welding Company are AC pulse current welders. The welding machine produced by the CARA-NDO Machinery Plant in the United States is a DC current welder, more specifically a secondary rectifier DC welder. This welder is the primary access control switch of the welding transformer and is output after secondary rectification. The technical and economic indicators of the welder are good, and various materials can be welded. There is no limit to the magnetic properties of the weldment and the assembly fixture, which can save 75% of the power and save energy. Taking the 142 4-3 automatic welding machine introduced by our factory as an example, the production speed of the machine is 600/hour, which is 5 times that of the domestic welding machine, and the transformer capacity is only 134kVA. The transformer capacity used in the domestic welding machine. isokVA, so it is an ideal welder.
Second, the basic principle of resistance welding
Resistance welding has two significant features: the use of an internal heat source, that is, the heat generated by the resistance of the current passing through the welding zone; the welding process must apply pressure, that is, under the action of pressure, after heating and then cooling to form a weld. In order to obtain proper resistance heat, the two welded parts must have an external power supply and always be welded under pressure. Therefore, the welding current I and the electrode pressure F are the most basic conditions for forming resistance welding. As for how the two parameters change and choose during the welding process, it depends on the material and the structural point of the workpiece and the welding equipment used.
1. Heat source for resistance welding
When a current passes through a conductor, it can be heated. If the resistance of the conductor is changed, the degree of heat generation can be changed. The amount of heat generated by the current through the weldment during resistance welding is determined by the Joule-楞 law:
Q=0.24IIRt
In the formula Q - the heat generated by the current (card, kilocalories); I-welding current (amperes); R - the resistance of the welded part (ohms); t-power-on time (seconds).
In the above formula, the welding current I and the welding time t are all preselectable conditions, and the resistance R is the basis of the internal heat source of the part. To study the internal heat source, we must first analyze the size, variation law and influencing factors of the resistance R.
2. Resistance of the welded part
Since spot welding, seam welding and projection welding used in steel drum production are lap welding resistance, the resistance R is determined by the internal resistance of the weldment R, the contact resistance of the weldment and the weldment, and the contact between the electrode and the weldment. The contact resistance R is composed, as shown in Figure 1.
R=2R piece + R touch ten 2R pole
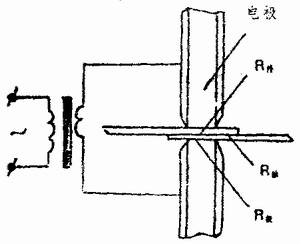
figure 2
(1) Contact resistance R touch
The surface of any part is not absolutely smooth, even if the surface of the welded part processed by the grinder is uneven under the microscope of 25 to 100 times, so the contact surface of the two weldments is always partially contacted under the action of the electrode pressure. See Figure 2. If the two weldments are connected to current, the current can only pass through the actual contact point, so that the cross section through which the current passes is small, while forcing the power line to bend and contract near the contact point, thereby forming contact resistance.
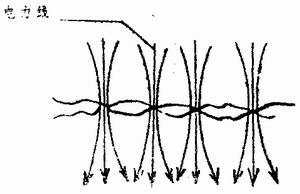
figure 2
Contact resistance is related to electrode pressure, material properties and surface condition, see Figure 3. As the electrode pressure increases, the convex point on the surface of the weldment is crushed, the oxide film is also destroyed, and the number and area of ​​the contact points are increased, so that the contact resistance is correspondingly reduced.
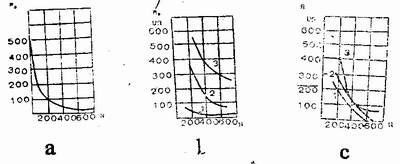
image 3
Also, if the material properties are softer, the crush strength is lower. The contact resistance is reduced due to an increase in the contact area.
When oxides and dirt are present on the surface of the weldment, especially oxides with low conductivity, the passage of current is severely impeded, and the contact resistance is significantly increased.
Figure 3 shows the relationship between contact resistance and electrode pressure, material properties and surface condition. Figure 3a shows a cleaned low carbon steel.
Figure 3b shows hard aluminum and hard aluminum. Curve 1 is a thickness of 1.5 + 1.5 mm and is cleaned by a steel brush; curve 2 has a thickness of 1.5 + 1.5 mm mm and is washed with orthophosphoric acid; curve 3 has a thickness of 0.5 + 0.5 orthophosphoric acid. Figure 3c shows the contact resistance between the electrode and the hard aluminum. Curve 1 thickness 1.5mm by steel brush cleaning multi-curve 2 thickness 1.5mm by orthophosphoric acid picking multi-curve 3 thickness 0.5mm by orthophosphoric acid pickling.
Contact resistance is temperature dependent. During the welding and heating process, as the temperature of the welded part of the weldment gradually increases, the crushing strength of the metal at the contact point gradually decreases, so that the contact area increases sharply and the contact resistance will rapidly decrease. Figure 4 shows the relationship between contact resistance and temperature between weldments when welding mild steel and hard aluminum.
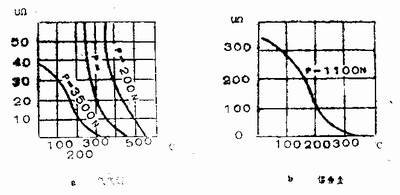
Figure 4 Relationship between contact resistance and temperature between weldments
It can be seen from the figure that the contact resistance of the steel weldment almost completely disappears when the temperature is close to 600 °C. For aluminum alloys, this temperature is around 350 ° C, and the time to reach this temperature is very short, generally not more than 0.4 seconds. Therefore, the contact resistance of the lap welding resistance has a certain influence on the heat generation at the beginning of the welding, and the proportion of the total heat forming the solder joint is not large. However, the heat generated by the contact resistance still plays an important role in the formation of the solder joint. Since the resistance of metal has the following relationship with temperature:
Rt=Ro(1+at)
Where: Rt - resistance at t ° C (Q); resistance at Ro-O ° C (Q); a - temperature coefficient of resistance. Aluminum copper is approximately equal to 0.004.
For steel, this coefficient a varies, that is, as the temperature increases, the electrical resistance of the metal increases. During the welding process, due to the contact resistance between the contact surfaces of the weldments, the metal on the contact surface between the weldments is first heated to a higher temperature, and the resistance of the weld metal is also greatly increased, so that the heat generated is rapidly increased. . At this time, although the contact resistance disappears, the metal first reaches the soldering temperature due to the continued action of the metal resistance heat of the weldment, thereby forming a weld uniformly distributed on both sides of the contact surface of the weldment.
(2) Contact resistance R pole of the weldment and the electrode. The presence of this resistor is an unfavorable factor affecting the soldering. If the R is very large, it is easy to overheat the weldment and the electrode, reduce the life of the electrode, and even burn the electrode and the contact surface of the weldment, which affects the quality of the seam weld. Before soldering, the electrode surfaces must be carefully cleaned to minimize the contact resistance between them. In addition, the resistor must also have good cooling conditions to cause the heat generated in the solder to rapidly dissipate.
(3) Internal resistance of the weldment. The internal resistance of the weldment can be calculated as follows:
R piece = K1, K2, δÏ/D
Where: δ——weld thickness; K1——uniform distribution coefficient of current density; K2——change coefficient of current density distribution due to uneven heating of weldment; Ï——resistance coefficient of weldment material (Q) .
It can be known from the above formula that the R piece has a close relationship with the resistivity of the material and a material having a large resistivity. (such as stainless steel), Rf+ is large, the heat is large at the same current; the small resistivity (such as aluminum alloy) R is small, at the same current, the heat is small. The R piece is related to the coefficient K1 of the uneven distribution of the current density. It depends on the value of δ/D and the electrode pressure F, and the effect between them on the R piece can be seen in Figure 5. K2 is the influence coefficient of the uneven heating of the weldment on the R piece. K2 should be between O. Between 75 and 0.95, when the temperature distribution is uneven, K2 takes a small value. The resistance of the welded part is an important factor in determining the quality of the weld and must be taken into account in the welding work.
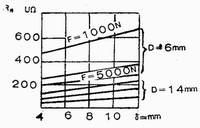
Figure 5
3. Diversion and its effect on welding. A part of the current that the resistance welding bypasses the weld zone is called shunting. Due to the presence of the split, the current through the weld is greatly reduced, resulting in insufficient heating, resulting in a decrease in the strength of the weld. Therefore, in order to obtain sufficient heat in the weld zone, we should consider the existence of the shunt when using the welding current, and increase the current appropriately.
In addition, the shunt also changes the current density distribution characteristics of each part of the weld zone, so that the contact between the electrode and the weldment has the largest current density. When the shunt is quite severe, even the current density at which the electrode is in contact with the weldment is larger than the rest of the area, thereby causing the weld metal to be rapidly added thereto, resulting in burn-through and external splash. In order to overcome this phenomenon, it is necessary to maintain a well-cleaned electrode surface, and to appropriately use a large electrode pressure or the like.
The Stitching Jewelry Box with advanced technology, exquisite and excellent product design which make the product more personalized and sophisticated. The vein on the surface greatly add to the aesthetic appeal of the box. It make the box more delicate.
Brand Name: Jinao
Place of Origin: Guangdong, China(mainland)
Surface Material: Customized
Inner Material: Velvet / foamed plastic
Color: Customized
Size: Multi-size + Customized
Feature: delicate / decorative
Logo Printing: Customized
Usage: Jewelry Box / Gift Box
Stitching Jewelry Box
Stitching Jewelry Box,Delicatestitching Jewelry Box,Stitching Leather Jewelry Box,Jewelry Packing Box
DongGuan Jinao Packaging Products Co., Ltd , http://www.jinaojewelrybox.com